
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.2, Problem 4T
At right is a free-body diagram for a cart. All foxes have been drawn to scale. In the Space below, sketch the cart, rope, etc., as they would appear in the laboratory.
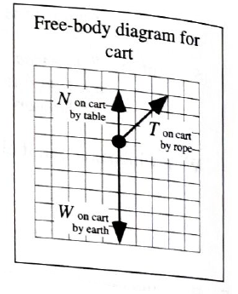
What can you say about the motion of the can based on the free-body diagram? For example, could the can be: moving to the left? moving to the right? Station? Explain whether each case is possible and, if so, describe the motion of the cart.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule01:06
Students have asked these similar questions
In your solutions, remember to do algebra first to derive equations and plug in values
for numerical solutions at the end.
1. A flatbed truck drives past you on a horizontal, flat road at 100 km/hr. Just when
it passes you, a crate falls off the truck and lands flat on the ground and travels 50
m before coming to a stop. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the road
and the crate. Assume that the initial speed of the crate is the same as the truck, 100
km/hr.
In your solution, include appropriate free body diagrams (FBD) for the crate, and
break up the forces acting on the crate into components either on the FBD or in a
table of the components.
The figure below shows a massless string wound around a spool of radius r. The mass falls with a constant acceleration, a. What is the equation for y in terms of θ and r? What is the equation for v in terms of ω and r? What is the equation for a in terms of α and r? Start from the expression for uniform acceleration in the y-direction for the falling mass and clearly show any steps or substitutions you make.
In the space to the right of the figure sketch a force diagram for the cart on the table.
Suppose that the hanging mass is 120g. Calculate the net force on the system.
If the mass of the cart was increased but the hanging mass remained the same, how would the acceleration be affected? Explain how you know in terms of net force and system mass.
If masses on the cart were moved from the cart to the hanger, how would the acceleration be affected? Explain how you know in terms of net force and system mass.
For a system mass of 600 g and a hanging weight of .5 N, determine the acceleration of the system.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 2.1 - Draw a large dot on your large sheet of paper to...Ch. 2.1 - Describe the remaining forces you have indicated...Ch. 2.1 - All forces arise from interactions between...Ch. 2.1 - There are many different types of forces,...Ch. 2.1 - Consider the following discussion between two...Ch. 2.1 - Label each of the forces on your free-body diagram...Ch. 2.1 - Sketch a free-body diagram for a book at rest on a...Ch. 2.1 - A second book of greater mass is placed on top of...Ch. 2.1 - Compare the free-body diagram for the lower book...Ch. 2.1 - Which, if any, Newton’s third law force pairs are...
Ch. 2.1 - A magnet is supported by another magnet as shown...Ch. 2.1 - An iron rod is held up by a magnet as shown. The...Ch. 2.2 - Compare the net force (magnitude and direction) on...Ch. 2.2 - Draw separate free-body diagrams for system A and...Ch. 2.2 - Is the magnitude of the force exerted on system A...Ch. 2.2 - D. Identify all the Newton's third law...Ch. 2.2 - Rank the magnitudes of the horizontal forces that...Ch. 2.2 - Suppose the mass of each brick is 2.5 kg, the...Ch. 2.2 - Describe the motions of systems A and B. How does...Ch. 2.2 - Compare the net force (magnitude and direction) on...Ch. 2.2 - Draw and label separate free-body diagrams for...Ch. 2.2 - Consider the following discussion between two...Ch. 2.2 - Rank the magnitudes of all the horizontal forces...Ch. 2.2 - Compare the magnitude of the netforce on system C...Ch. 2.2 - Draw and label a free-body diagram for system C....Ch. 2.2 - At right is a free-body diagram for a cart. All...Ch. 2.3 - Describe the motions of block A, block B, and the...Ch. 2.3 - On a large sheet of paper, draw a separate...Ch. 2.3 - Identify all the Newton's third law...Ch. 2.3 - Rank, from largest to smallest, the magnitudes of...Ch. 2.3 - Consider the horizontal components of the forces...Ch. 2.3 - If the motion of the blocks is the same as in...Ch. 2.3 - Suppose the mass of the string that connects...Ch. 2.3 - A string exerts a force on each of the two objects...Ch. 2.3 - If you know that the net force on a massless...Ch. 2.3 - Predict the subsequent motions of objects A and B...Ch. 2.3 - Draw separate free-body diagrams for objects A and...Ch. 2.3 - Predict: • what will happen to object C when it is...Ch. 2.3 - Draw and label separate free-body diagrams for...Ch. 2.3 - The weight of a 200 g mass has magnitude...Ch. 2.3 - Consider the following statement about the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
24. Which travels more slowly in glass: red light or violet light?
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
34.101 Focal Length of a Zoom Lens. Figure P34.101 shows a simple version of a zoom lens. The converging lens h...
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
The magnitude and direction of ball’s velocity at 0.250 s .
Physics (5th Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk(*) desig...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
25. The wings of the blue-throated hummingbird, which inhabits Mexico and the southwestern United States, beat ...
College Physics (10th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For every problem, show FBDS and write down Newton's 2nd law in component form. Remember to be precise in your work: clearly describe what your system of interėst is, pay attention to vector/component notation, and follow a clear strategy in your work-the layout of your page should reflect a linear progression of steps and thoughts (please do not jolt down things all over the place!!); show all details of the calculations that are needed to answer the questions: no guesses of course! A block with mass M is pushed against a vertical wall with a force of magnitude P and directed at an angle 0 below the horizontal. The wall and the block experience friction (coefficient of static friction is Hs). Is it possible to keep the block from sliding downward? And if so, how exactly? Use Newton's 2nd law to support your answer. Marrow_forwardd. What is the acceleration of the box? (magnitude and direction) e. One of the forces on your free body diagram should be the normal force (make sure it is there!). For the normal force, what is the object, and what is the agent? f. Is there a Newton's third law force pair associated with the normal force acting on the box?arrow_forwardThe device diagramed in the figure below is called an Atwood's machine. Let m1 = 2kg and m2 = 4 kg. Assume the pulley to be frictionless and massless. How far will m2, fall in time t = 0.5 s after the system is released? What is the tension in the light cord that connects the two masses?arrow_forward
- Consider the information in the image below. Write the net force equation the axis perpendicular to the plane . Then solve for the normal force in terms of the weight of the box, mgand the angle of inclination, such as mg cos(?) Make it clear on your diagram how the angle is used in finding force componentsarrow_forwardClick on the image below to launch the video: Unfair Race. Once you have watched the entire video, answer the graded follow-up questions on the right. You can watch the video again at any point. PEARSON reset ALWAYS LEARNING This video shows the results of releasing a frictionless box and a rolling disk with equal masses from the top of identical inclined planes. Part B How much sooner does the box reach the bottom of the incline than the disk? Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables m, h, 0, and R, as well as the acceleration due to gravity g. ► View Available Hint(s) ΨΗ ΑΣΦ/Φ Submit Previous Answers ? X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remainingarrow_forwardWhich way and by what angle does the accelerometer in figure deflect under the following conditions? The cart is moving toward the right with speed increasing at 2.0 m/s2. (Express your answer in degrees. Enter positive value if the accelerometer deflects to the left of vertical and negative if it deflects to the right.) The cart is moving toward the left with speed decreasing at 4.5 m/s2. (Express your answer in degrees. Enter positive value if the accelerometer deflects to the left of vertical and negative if it deflects to the right.) The cart is moving toward the left with a constant speed of 4.0 m/s. (Express your answer in degrees. Enter positive value if the accelerometer deflects to the left of vertical and negative if it deflects to the right.)arrow_forward
- With air resistance being a significant factor, compare the magnitudes of the accelerations experienced by five identically shaped and sized balls, as depicted in the given diagram below. The velocity shown are instantaneous. Arrange the accelerations from highest to lowest and consider the possibility of equality between some values. Then, explain the reasoning of your ranking. Note in answering: Type your answer like A = B, C, D, E. (A = B and ranked 1st) 50 g Just released 1₂=0 100 g Just released v₂ = 0 50 g 100 g vy=-20 m/s vy=-20 m/s v₂ = 20 m/s 50 garrow_forwardSHOW COMPLETE AND CLEAR SOLUTION. PROVIDE FREE BODY DIAGRAM (FBD). EXPLAIN THE COMPUTATIONS SO THAT I CAN UNDERSTAND. Obtain the resultant of the six forces acting on the sides of a hexagon. Each side measures 125 mm.arrow_forwardFor the given several questions, consider the dot diagram below for the motion of an object along a horizontal surface. The motion is divided into several time intervals, each labeled with a letter. 1. During which time interval(s), if any, are there no forces acting upon the object? List all that apply. 2. During which time interval(s), if any, are the forces acting upon the object balanced? List all that apply. 3. During which time interval(s), if any, is there a net force acting upon the object? List all that apply. 4. During which time interval(s), if any, is the net force acting upon the object directed toward the right? List all that apply. 5. During which time interval(s), if any, is the net force acting upon the object directed toward the left? List all that apply.arrow_forward
- Show all of your work. A 50 kg box is being pulled to the right across the floor as shown. a) Describe two free body diagrams: one without resolving components, and one with (only) resolved components. b) Apply Newton’s 2nd Law along the x-direction. Calculate the acceleration of the box along the floor. c) Apply Newton’s 2nd Law along the y-direction. Calculate the normal force upon the box.arrow_forward**18. A block slides down an inclined ramp, speeding up as it goes. The ramp is not friction less (u0.50). The ramp makes an angle of 53° with respect to the horizontal, as shown at right a) Draw a free-body diagram for the block. Label your forces using the method explained on page 85 b) If the magnitude of the normal force is 90 N, find the mass of the block 530 c) Find the acceleration (magnitude and direction) of the block. 1arrow_forwardThe diagram below shows a mass that is oscillating on the end of a string at three different times t₁, t2, and t3 during a single cycle. At t, it is at maximum displacement in the negative direction. In the following questions we will disre- gard the centripetal acceleration of the bob due to its circular motion about the point O. a. Draw the velocity and acceleration vectors next to the pendulum bob at times t₁, t2, and t3 to show the direction and relative magnitude of those vector quantities at those positions. The vectors at time t₁ have already been drawn. Note: The centripetal acceleration that arises from the circular motion about O is neglected. Draw the forces acting on the bob at each of those instants. 11 a V At which instant t₁, t2, or t3 does the bob have the greatest velocity? What is the acceleration at that position? Explain. b. C. Figure 11-3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Newton's Third Law of Motion: Action and Reaction; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y61_VPKH2B4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY