
Concept explainers
An iron rod is held up by a magnet as shown. The magnet is held up by a string.
1. In the spaces below, sketch a free-body diagram for the iron rod and a separate free-body diagram for the magnet.
The label for each of the forces on your diagrams should indicate:
- the type of force (e.g., gravitational, normal),
- the object on which the force is exerted, and
- the object exerting the force.
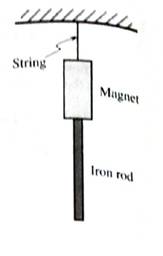

2. For each of the forces shown in your diagram for the iron rod, identify the corresponding force that completes the
3. How would your diagram for the iron rod change if the magnet were replaced with a stronger magnet? Which forces would change (in type or in magnitude)? Which forces would remain the same?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 2 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
- 1. Your free body diagram for Part 1 should have looked it this. F. max Drag and drop the heads and tails of the vectors to construct the free-body diagram. Note: the applied force is directed to the right. Note: the angles may be within ±15°, and the magnitudes are not considered. = Suppose you have a 120-kg wooden crate resting on a wood floor. Use µg = 0.5 and μ = 0.3 . Assume all quantities are correct to 3 significant figures. a = 1.96 ffric; 180° (b) What is the maximum force you can exert horizontally on the crate without moving it? Enter to 3 significant figures ✔N N: 90° a m/s² mg; 270° F:0° (c) If you continue to exert this force once the crate starts to slip, what will its acceleration then be? Enter to 3 significant figuresarrow_forwardPlease explain and show your solution. Choose from the choices below. Thank you.arrow_forwardAll please Three masses are connected as shown in the figure below. The hanging blocks fall as the mass on the frictionless table accelerates to the right. Use this information to answer the next 4 questions. You should assume that the ropes and pulley are massless and the pulley is frictionless. (m1 = 3kg; m2 = 1kg; and m3 = 5kg). 1. What is the free body diagram for mass 2? 2. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of mass 1? 10.2 m/s^2 13.7 m/s^2 6.5 m/s^2 9.8 m/s^2 1.4 m/s^2 3.3 m/s^2 3. What is the magnitude of the tension in the rope connecting mass 1 to mass 2? 29.4 N 19.6 N 58.8 N 41.1 N 5.10 N 16.3 N 4. What is the magnitude of the tension in the rope connecting mass 2 to mass 3? 19.6 N 29.4 N 41.1 N 58.8 N 5.10 N 16.3 Narrow_forward
- Constants The figure(Figure 1) shows a block (mass ma ) on a smooth horizontal surface, connected by a thin cord that passes over a pulley to a second block (mB), which hangs vertically. Part B Draw a free-body diagram for block B, showing the force of gravity on it, the force (tension) exerted by the cord, and any normal force. Draw the vectors starting at the black dot. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded. Figure (1 of 1 mB No elements selectedarrow_forwardProblem Solving: Show your solutions completely and neatly. 1. Two blocks A and B are lying on a frictionless surface as shown in Figure below, are connected by a cord passing over a small frictionless pulley. a. Draw an FBD for each block. b. What is the tension in the cord? 10 Kg A 30° 45° c. Calculate the mass of block B which slides down the plane that keeps the system moving at a constant speed.arrow_forwardPROBLEM SET # 7: THE EQUILIBRIUM MODEL On the space provided, present correct and organized solutions to the following answered problems. Box the final answers. Detach each page neatly and submit to your instructor. 2. Block B hangs on a cable connected block A through a pulley as shown in the figure below. The two blocks are in equilibrium. Block B has a mass of 2.5 kg and the angle of the incline 6 is 35°. (a) What is the tension on the cable? (Ans: 24.5 N) (b) What is the mass of block A? (Ans: 4.36 kg)arrow_forward
- For this question you may draw diagrams if necessary to explain your answer. 1. a. Explain clearly Newton's First Law, Second Law and Third Law of motion. b. Give two real life examples for each of the law. c. A rocket moving in space at uniform velocity explain why the net force on the ship is zero or E F = 0. d. Explain how the rocket can change direction.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a massless string wound around a spool of radius r. The mass falls with a constant acceleration, a. What is the equation for y in terms of θ and r? What is the equation for v in terms of ω and r? What is the equation for a in terms of α and r? Start from the expression for uniform acceleration in the y-direction for the falling mass and clearly show any steps or substitutions you make.arrow_forwarduse the GRAPHICAL METHOD to solve the given problem below to recall what you have discussed in physics about the head-to-tail rule of constructing vector/force diagrams and about Newton’s 1st Law of motion.An electric light fixture weighing 15 N hangs from a point C, by two strings AC and BC. The string AC is inclined at 60° to the horizontal and BC at 45° to the horizontal as shown, determine the forces in the strings AC and BC.1. What scale did you use?2. What is the force in string AC?3. What is the force in string BC?arrow_forward
- The previous step focused on friction for horizontal surfaces. As we discussed above, angled surfaces like the wedge below have different considerations. FN = mg cos(0) F₁ = mg F₁ = ? F₁ = ? Fy=mg cos(0) Specifically, we have the following considerations. 1. The normal force is not equal to mg. 2. There is a force acting along the angle of the wedge due to gravity. What is the coefficient of static friction ? Fx = mg sin(0) Let's consider the implications of this type of problem with the following examples. For all of the examples, the box has a mass of 25 kg. Imagine the box is on a surface that allows you to adjust the incline angle, 0. You find the maximum angle where the box remains stationary. That is, at any higher angle, and the box begins to slide. The static friction force at this maximum angle is 150 N. What is the angle 0 (in degrees)? Now you raise the incline to an angle of 60° greater than the angle of maximum static friction found above. At this angle, the box slides…arrow_forwardAnalyze the problem below then answer the following questions B. What is the magnitude of the Torce in standard form? The following force vectors are acting on an object from different directions. A = (101 – 50k)N, B = (301 + 25/)N, and ĉ = (-15) + 20k)N. .Roundoff at three decimal places, e.g. "233.401N"No space between characters and if answer A.What is the resultant vector in unit vector form? is whole number, no need to add decimal places. If answer is too large or too smallI (more than 1,000,000 or less than 0.0001) .Write answers without the express answer as Scientific "hat", refer to exact example notation in exact sample format "3.2€23N" or "3.2e-15N" or format "(-7i+2j-3k)N" No spaces "-3.2€15N". This format means between characters. If result is 3.2x102"N etc. "Ik", omit the number “1". If the component is zero, no need to Your answer write. Your answer (c.What is the angle and direction of the vector along the x-y plane? DWhat is the angle and direction of the vector along…arrow_forwardPROBLEM SET # 8: PARTICLE UNDER A NET FORCE On the space provided, present correct and organized solutions to the following answered problems. Box the final answers. Detach each page neatly and submit to your instructor. A 2.5-kg concrete block sliding on a vertical wall is being acted upon by a force P as shown in the figure below. Assume that the coefficient of kinetic friction between the 2. concrete block and the wall is 0.88. 148° (a) Draw the free-body diagram of the concrete block. (b) If the normal force exerted by the wall to the concrete block is 20.0 N, what would be the magnitude of the external force P, and (Ans: 37.74 N) (c) The acceleration of the block? (Ans: -15.56 m/s)arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





