
Concept explainers
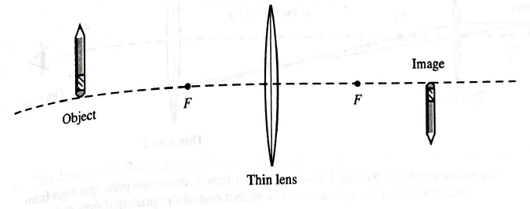
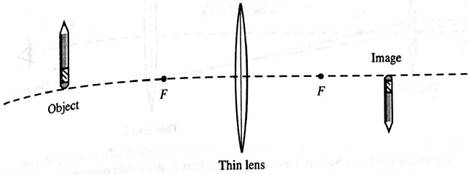
Reproduced below is a side view diagram of the situation described in section II of the tutorial.
Determine an expression for the lateral magnification,
To calculate:.
The expression for the lateral magnification
Answer to Problem 1TH
The expression for the lateral magnification is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
An object is placed before a thin lens as follows :
Formula used :
In similar triangles ABC and DEF , corresponding sides are in equal proportions or,
AB / BC = DE / EF
AB / AC = DE /DF
Calculation:
Ray diagram showing the principal ray from the tip of pencil that is object, is given below;
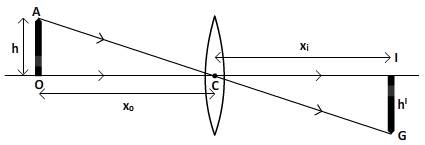
In the above diagram, two triangles given that are
are similar.
So that,
Here,
And,
Therefore,
Hence, lateral magnification is given below;
Conclusion:
Therefore, the lateral magnification,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
University Physics Volume 1
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
- Suppose you have a concave mirror as shown in the image below. If h = 1.6m is the height of an object (really the displacement of the top of the object from the axis) and h' = 4.05m is the height of the image, what is the magnitude of the transverse magnification (in units of meters)? Image Object Note: Do not explicitly include units in your answer (it is understood the unit is meter). Enter only a number. If you do enter a unit, your answer will be counted wrong.arrow_forwardYou hold a spherical salad bowl 50 cm in front of your face with the bottom of the bowl facing you. The salad bowl is made of polished metal with a 48 cm radius of curvature. Part A Where is the image of your 5.0-cm-tall nose located? Follow the sign rules. Enter the magnitude of the distance from the salad bowl. Express your answer with the appropriate units. s' Submit Part B Value y' = Request Answer What is the image's size? Express your answer with the appropriate units. μА Units Value Units ? ?arrow_forwardin step 1 why is the image distance -4 cm?arrow_forward
- In the figure below (not to scale), the focal lengths of the thin converging lenses, L1 and L2, are 20.0 cm and 10.0 cm, respectively. L1 L2 When object O is placed 30.0 cm to the left of L1, its image forms 7.0 cm to the right of L2. What is the distance between the two lenses? Express your answer to the nearest cm.arrow_forwardCase Example:On one wall there hang a picture 6 ft. x 4 ft. in dimension. On the opposite wall 15 ft. away is a plane mirror. What is the minimum size of the mirror for aperson who is standing 8 ft. away from the mirror to see the whole picture? (The solution is on the picture)Now, please answer questions 1 and 21. Compute for the number of images produced by a 2 separate mirrors at an angle of 45 degrees if the object is placed between the mirrors.Formula:N = (360/Angle) – 12. A sight testing chart measuring 120 cm x 80 cm, the long dimension being the vertical one is to be viewed by reflection in a plane mirror. Find the smallest size of the mirror that can be used if the chart is 3.25 meters away from the mirror and the observer’s eye is 2.75 meters away from the mirror. The lower edge of the chart is 1.5 meters above the ground. How high must the edge ofthe mirror from the ground?arrow_forwardThe diagram below shows the situation described in the problem. The focal length of the lens is labeled f; the scale on the optical axis is in centimeters. Draw the three special rays, Ray1, Ray2, and Ray3 as described in the Tactics Box above, and label each ray accordingly. Draw the rays from the tip of the object to the center vertical axis of the lens. Do not draw the refracted rays. Draw the vectors for the incident rays starting at the tip of the object to the center vertical axis of the lens. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. Vectors: Ray3 Ray though center of lens Ray2 Ray through near focal point Rayl Ray parallel to axis Unlabeled vector Objectarrow_forward
- Two plane mirrors are at an angle of ?1 = 57.6° with each other as in the side view shown in the figure below. If a horizontal ray is incident on mirror 1, at what angle ?2 does the outgoing reflected ray make with the surface of mirror 2?arrow_forwardEstimate the magnification and focal length of the pitcher of water shown in the figure below. (Assume that the tree is about 57 ft tall and its inverted image is about 1 foot tall. Also assume that the tree is about 210 ft from the pitcher. Include the sign of the value in your answers.) magnification focal length X The response you submitted has the wrong sign. ft 3.57 Elizabeth Owens/American Association of Physics Teachersarrow_forwardSuppose you know the six cardinal points of an optical system (two focal points F1 and F2, two principal points H1 and H₂ and two nodal points N₁ and N₂), complete the three special rays to locate the image position formed by this system. Label the focal lengths, object distance and image distance. [Hint: A ray parallel to optical axis, turns to the focal point F2 after passing through the principle plane H₂. A ray through Fi will turn to parallel after H₁. A ray moving towards to N₁ will emerge at N₂ with the same angle. In a thick lens, N overlaps with H point if the refractive index is the same on both sides of the lens.] F₁ H1 N₁ H₂ N₂ F₂arrow_forward
- In order to measure focal length of a diverging lens (L2), we set up the following experiment (as shown in the right figure). It uses another converging lens (L1). An object (o) is placed in front of lens (L1). The image of the object can be seen on a screen (S,), which is located 20cm behind lens (L2). Next, after removing lens (L2) only, the image can be restored (seen) by moving screen 5cm toward lens (L1) to a new location of S2. Please compute the focal length of lens (L2). L, L2 S2 5cm 20cmarrow_forwardUsing a ruler or any straight edge and a scale of your choice and applying the steps in ray diagramming, complete the ray diagramming for Cases 2 to 5 in order to prove the correctness of the image characteristics of the objects in the specified positions as indicated in Table 1.arrow_forwardYou hold a spherical salad bowl 60 cm in front of your face with the bottom of the bowl facing you. The salad bowl is made of polished metal with a 40 cm radius of curvature. Part A Where is the image of your 5.0-cm-tall nose located? Follow the sign rules. Enter the magnitude of the distance from the salad bowl. Express your answer with the appropriate units. = Submit Part B μÅ y' : = Value Request Answer What is the image's size? Express your answer with the appropriate units. μĂ Units Value Units ? ?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





