
Concept explainers
Core Skill: Connections Look back to Figure 32.14 to see a more detailed illustration of the flowering plant life cycle. How can you recognize and where can you find the gametophyte generation of a flowering plant?
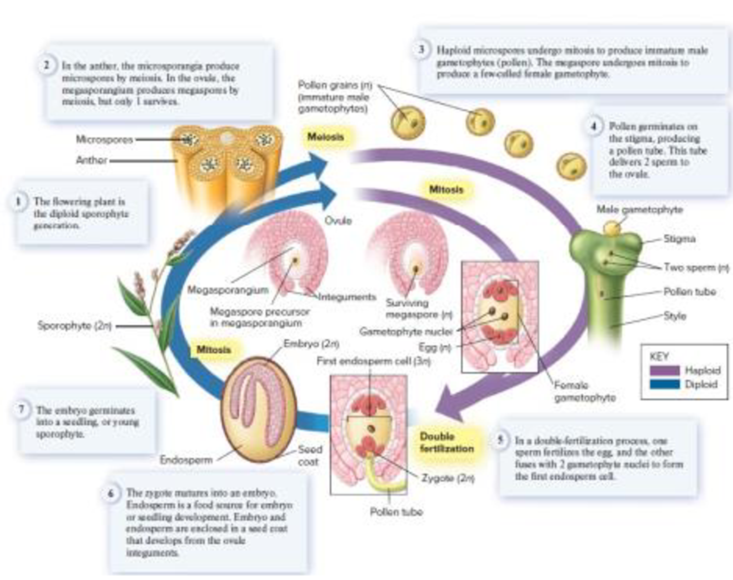
Figure 32.14 The life cycle of a flowering plant, illustrated by the genus Polygonum. Flowering plant life cycles differ in length and in the number of cells and nuclei occurring in the female gametophyte, with the seven cells and eight nuclei of Polygonum being common.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 40 Solutions
Biology
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Biology Illinois Edition (Glencoe Science)
Evolutionary Analysis (5th Edition)
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Plus Mastering A&P with eText - Access Card Package (10th Edition) (New A&P Titles by Ric Martini and Judi Nath)
Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy (5th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (4th Edition)
- Exercise 2: Construct an indented dichotomous key on the following groups of plants: Bryophyta Lower Vasuclar plants Higher Vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Pteridophyta Equisetophytaarrow_forwardPostlab: Bryophytes, Seedless Vascular Plants & Gymnosperms 1. What is the conspicuous form of the bryophytes? Is this form haploid or diploid? 2. The part that produces the male gametes is called the....? 3. The part that produces the female gametes is called the... 4. Spores are produced by which cell division process? 5. What is the conspicuous form of the seedless vascular plants? Is it haploid or diploid? 6. What are microspores? Where are they produced in gymnosperms? 7. Megaspores give rise to which structure in gymnosperms? 8. How are most gymnosperms pollinate d? 9. In gymnosperms, the material that nourishes the embryo derives from what tissue? 10. How can you visually differentiate a male from a female cone in pines?arrow_forwardActivity_BIO 100 (Slide 2 of 3: Pollination vs Fertilization) Luis Carlos Ahuage CC Using Doodling, mark-- using the two flowers-- your explanation for the differences between Pollination and Fertilization tip: be sure not to cause self-fertilization in your flower! Stigma -Stigma Anther Carpel Anther Carpel Stamen Stamen- Style Ovary Ovule Style Ovary Ovule Filament Filament Petal Petal (petals = corolla) (petals corolla) %3D Sepal (sepals = calyx) Receptacle Sepal (sepals = calyx) Receptacle Peduncle Peduncle You have 8 minutes TOTAL to complete 3 slides. Do not save your recording yet, MOVE TO THE NEXT SLIDE... 0:00 / 0:00 O 1 nere to search 09arrow_forward
- Examine the shoot system of a mature plant (Coleus blumei). Identify the shoot tip, nodes, internodes, leaves, and axillary buds. Each unit of stem that consists of a leaf, axillary bud and internode is referred to as a phytomere. Note that axillary buds always occur above a leaf. Axillary buds give rise to branch shoots. Thus, branching in a shoot system is exogenous (of external origin). How does this compare to branching in a root system?arrow_forwardINSTRUCTION: Answer the question in simple words and that is easy to comprehend. (ESSAY) QUESTION: How are the gametophytes of seedless vascular plants similar to the gametophytes of bryophytes? How are they different?arrow_forwardPLANT VOCABULARY DOMINANT GENERATION Sporophyte/Gametophyte CELL TYPE IN ADULT ORGANISM Haploid = Diploid= VASCULAR TISSUES PRESENT Phloem = Xylem = MALE SEX CELLS/IS WATER NEEDED? Pollen = Anther = FEMALE SEX CELLS FLOWERS? Ova = Ovary = SEEDS "NAKED" OR IN FRUIT? Seed = Fruit= ROOT SYSTEM PRESENT AND TYPE? Rhizome Tuber Coniferophyta hour IN COVAS 150 XXX11 Monocot VEZIR 03 Eudicotarrow_forward
- LEAF TYPE AND ARRANGEMENT Instruction: 1. Match the given photos with the following leaf characteristics 2. Name the plant species and draw their specific leaf Betel Papaya Ixora Cogon grass Cassava River tamarind Lavender sorrell A. Hibiscus a) Simple chordate leaf Name of species: Diagram: b) Simple peltate leaf Name of species: Cananga Golden trumpet Diagram: Simple linear leaf Name of Diagram Palmately compound leaf Name of species: Diagram: Paripinnate compound leaf Name of species: Diagram: f) Imparipinnate compound leaf Name of species: Diagram: g) Opposite leaf arrangement Name of species: Diagram: h) Alternate leaf arrangement Name of species: Diagram: i) Whorled leaf arrangement Name of species: Diagram: j) Spiral leaf arrangement Name of species: Diagram: c) species: d) e)arrow_forwardExplain what plant specific biological process can be researched with plants that have a free-living gametophyte stage in their life cycle and possible benefits of researching plants with a life cycle that has a dominant gametophytic phase.arrow_forwardACTIVITY &8: Fruit and seed anatomy (Student dissection or demonstration) The fate of the parts of the flower can differ among angiosperms. Floral parts typically become part of the seed and/or the fruit. 1. Obtain a germinated bean and use p. 145 of the atlas as a guide. The pod that housed the bean is the fruit of the bean plant. The bean is the seed of the plant. 2. The papery outer red covering of the bean is the seed coat, which developed from the integuments of the ovule. g eno le al boez 3. The white structure on the internal region of the bean is the hilum, the site where the seed was attached to the inner walls of the pod. eliunt ynd Vhutem Js 4. Draw and label the exterior of the bean in the space provided. U CLO22-26Cpou 5. Remove the seed coat to expose the pale underlying structure (cotyledon). Gently pry open the bean. How many cotyledons does a bean have? 6. Once the bean is opened, the embryonic sporophyte is revealed. It consists of a "leaf- like" structure called the…arrow_forward
- READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS: Bryophytes in which the gametophytes are "leafy" in appearance and the sporophytes grow conspicuously from the tips of the gametophyte plants. STEP 1: Examine the mass of moss plants and then select one or two individual gametophyte plants and note the leaf-like (not true leaves because they lack conducting tissue) structures which are arranged around a central, vertical "stem-like" stalk and root-like rhizoids which anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients. STEP: The sex organs are in the tips of the plants and must be seen with the microscope. Study a slide of a vertical section through head of a mate plant and note the many antheridia. STEP 3: Examine a slide through a vertical section of a female plant. Note the many upright archegonia each on a tall stalk and each with a swollen base or venter containing an egg and an elongate neck. Note the filamentous paraphyses between the archegonia. STEP 4: Examine a living or preserved…arrow_forwardLeaves Dichotomous Key Using the provided dichotomous key, determine the latin name for each of the leaves below. Dichotomous Key for Leaves 1. Compound or simple leaf 1a) Compound leaf (leaf divided into leaflets) .go to step 2 1b) Simple leaf (leaf not divided into leaflets) go to step 4 2. Arrangement of leaflets 2a) Palmate arrangement of leaflets (leaflets all attached at one central point) ....Aesculus (buckeye) 2b) Pinnate arrangement of leaflets (leaflets attached at several points) ...go to step 3 3. Leaflet shape 3a) Leaflets taper to pointed tips .Carya (pecan) 3b) Oval leaflets with rounded tips IV Robinia (locust) 4. Arrangement of leaf veins 4a) Veins branch out from one central point ....go to step 5 4b) Veins branch off main vein in the middle .go to step 6 of the leaf. 5. Overall shape of leaf 5a) Leaf is heart-shaped..Cercis (redbud) 5b) Leaf is star-shaped VI VI ..Liquidambar (sweet gum) 6. Appearance of leaf edge 6a) Leaf has toothed (jagged) edge .Betula (birch)…arrow_forwardPlant Diversity Know the phylum, domain and supergroup of land plants and its sister taxon. Describe at least four out of the seven derived traits of land plants. Describe and draw a general land plant life cycle (know the terms haploid, diploid, gametophyte, sporophyte, spore, meiosis, mitosis)arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
